The temperate rainforest
![[object Object]](https://d2ijqnyf2ixq2j.cloudfront.net/media/general/Test%20f%C3%BCr%20Jan/Bildschirmfoto%202023-12-11%20um%2017.17.12.png)

Globe + Where is the temp. RW located?
What is the temperate rainforest?
The temperate rainforest is a unique forest ecosystem. Due to its geographical location, it is not as hot here as in the tropics and you can find different animal and plant species.
...
Graphic #1: Development of temp. RW
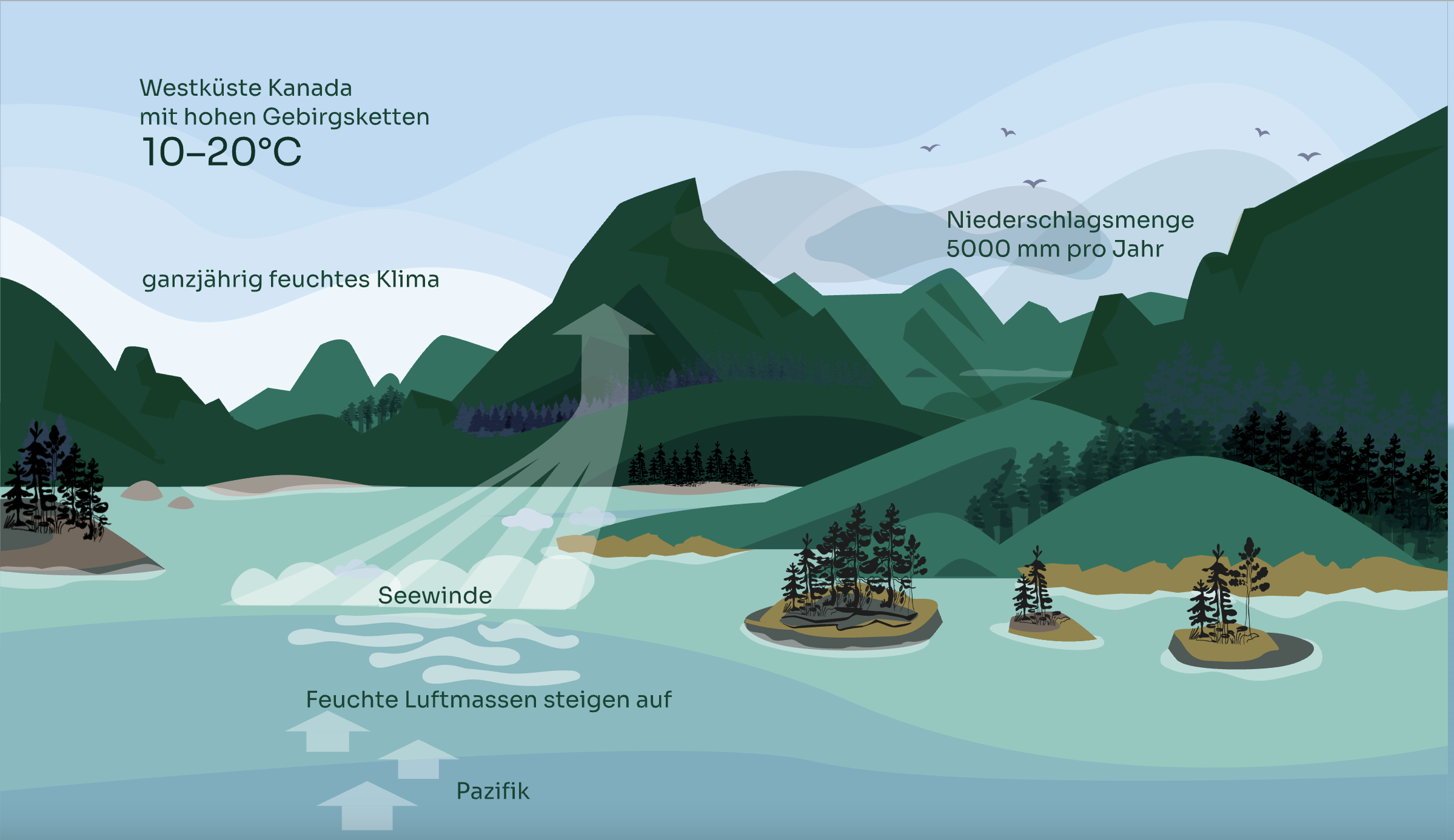
How do temperate rainforests develop?
Rainforests develop in a year-round humid climate with particularly high levels of precipitation. Almost all temperate rainforests are located on the western side of high mountain ranges, including the temperate rainforest of western Canada.
...
Important - and threatened
The primeval forests of the temperate rainforest are the most species-rich ecosystem in the temperate climate zone and are therefore an important habitat. They also store vast amounts of carbon and therefore play an important role in the global climate system.
Unfortunately, however, these primeval forests are under acute threat from deforestation and urbanization. That is why Wilderness International is active in the temperate rainforest. Here you can help us preserve a piece of Canadian old-growth forest forever:

The primeval forests of Western Canada are home to wild coastal wolves, mighty bald eagles, rare carnivorous sundews and gigantic primeval forest giants such as maple trees, Alaskan cedars and giant live trees, up to 2,000 years old and 100 meters high.
Episode 3: Trees (release planned for 18.12.)
What makes it so special?
1. Huge, ancient trees
Due to the mild, humid climate and the low human influence, evergreen tree giants grow for up to 2000 years. These include the giant arborvitae, the Sitka spruce and the Douglas fir. Some trees reach heights of over 100 meters. They make up the majority of the total biomass of up to 1,000 tons per hectare - which even surpasses tropical forests.
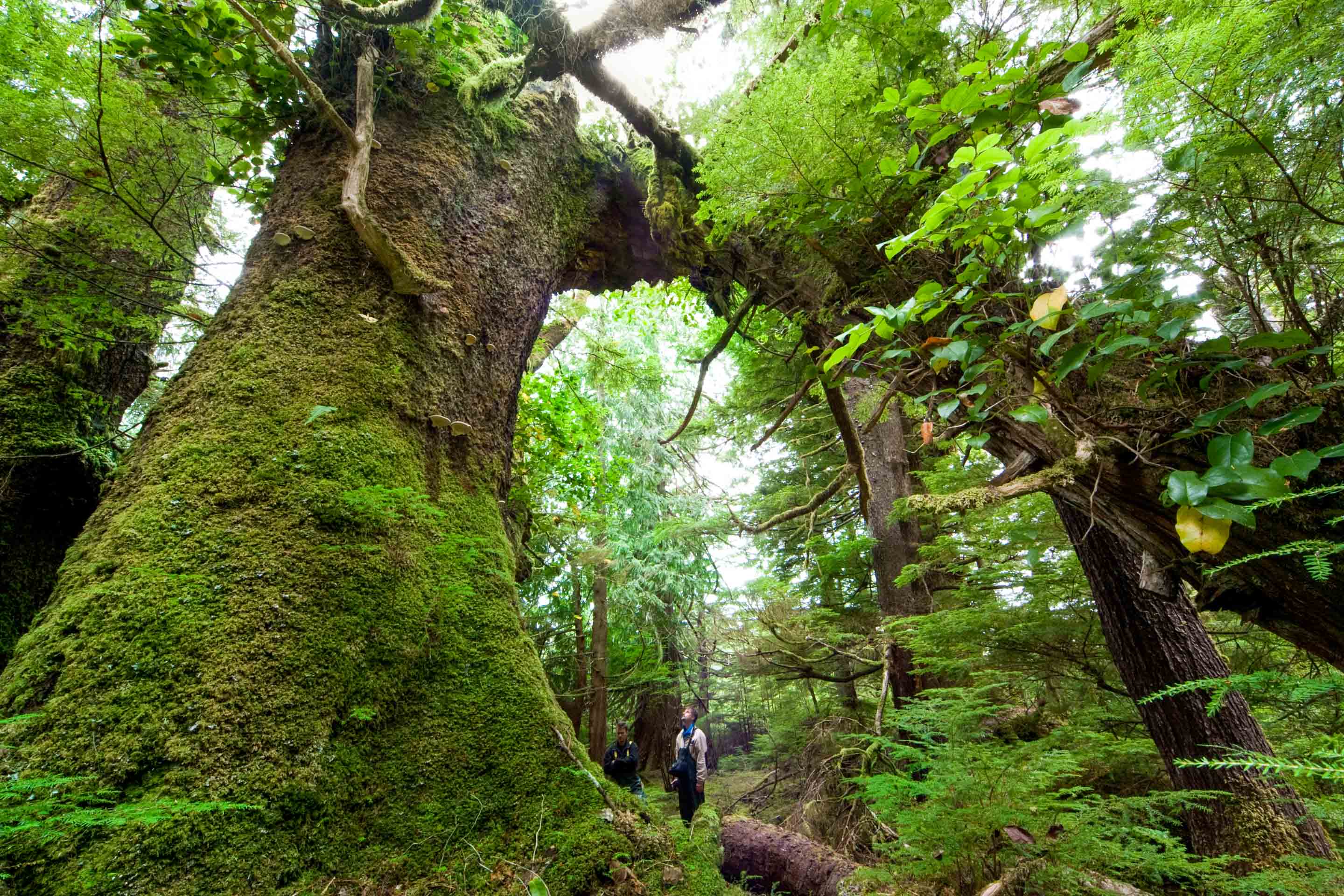

How can the trees grow so big and old?
Mild climate
The Pacific Ocean with its gigantic masses of water acts as a heat reservoir. Particularly in the winter months, the water releases a lot of heat energy, which leads to extremely mild and short winters. Due to this balanced climate, the growing season is unusually long and frost is rare. Plant parts that die and fall to the ground are converted into new nutrients throughout the year in biochemical decomposition processes.
Lichens
The treetops are home to epiphytes such as mosses and ferns. Due to the good air quality and high humidity, many lichens such as beard, crust and lung lichens also colonize temperate primary rainforests. Lichens are a symbiosis of a fungus and an alga. The fungus provides the body, the algae carries out the photosynthesis. The lichens are blown down by storms and fall to the forest floor, where they release their nutrients.
Sufficient water
In addition, the Pacific winds bring an extremely large amount of water into the forest, which in turn can be stored in the thick layer of moss and in the forest floor. Thanks to this optimal supply of nutrients and water, countless other plants such as lichens, mosses and fungi grow alongside the trees, which in turn die off at some point. This creates a continuous cycle in which each species contributes to an intact ecosystem.
Tree habitat
If you protect 64 m2 of forest with us, for example, then it's not just about the surface area. Much more important are the hundreds of cubic meters of habitat that open up above this area up to the greatest heights. Some giant trees can grow up to 100 m high. This means they offer plenty of habitat for numerous animals and plants. And above all, the numerous niche habitats on the branches offer perfect conditions for a wide variety of perching plants and animals.
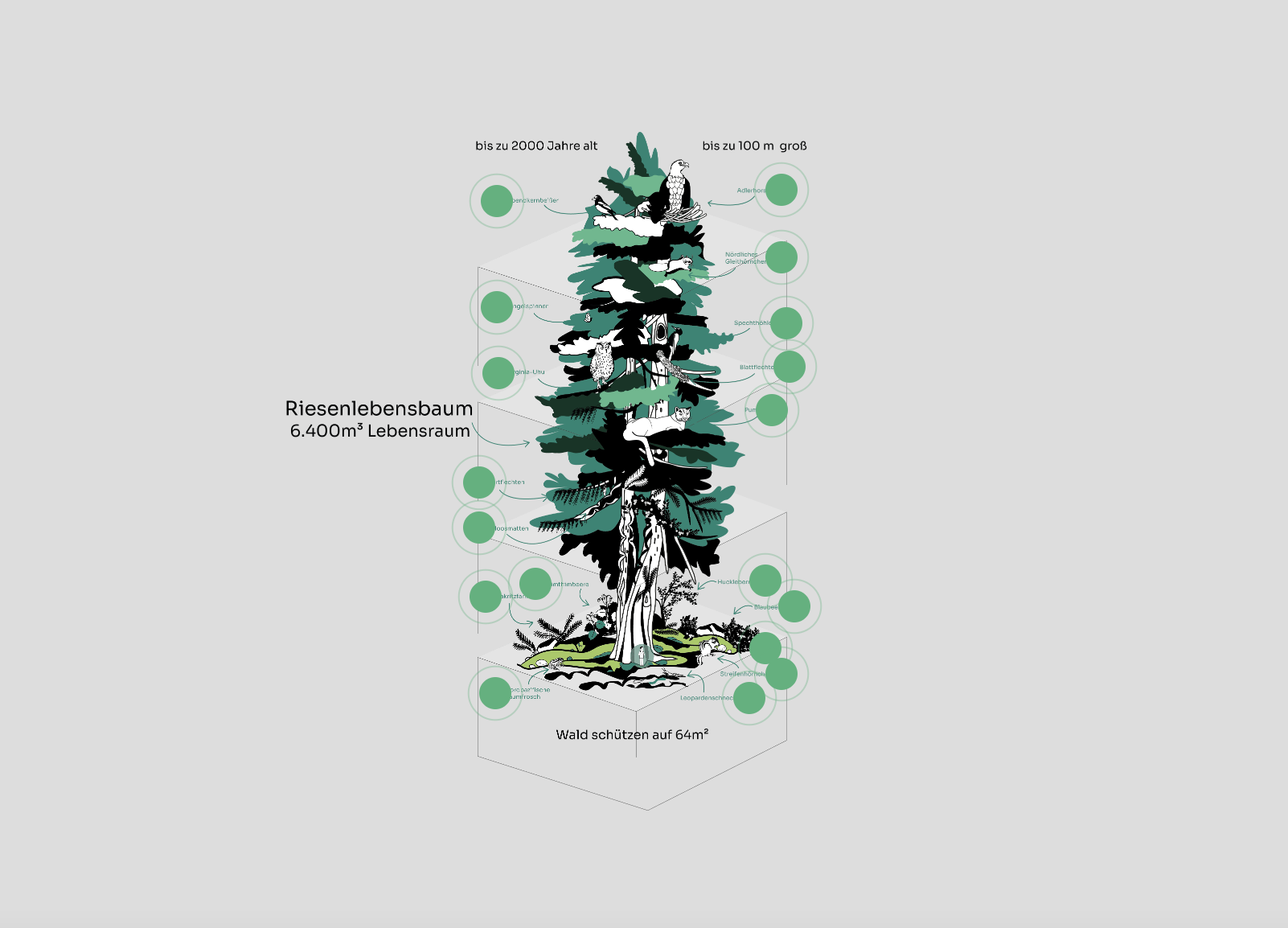
Figure 2 Tree habitat
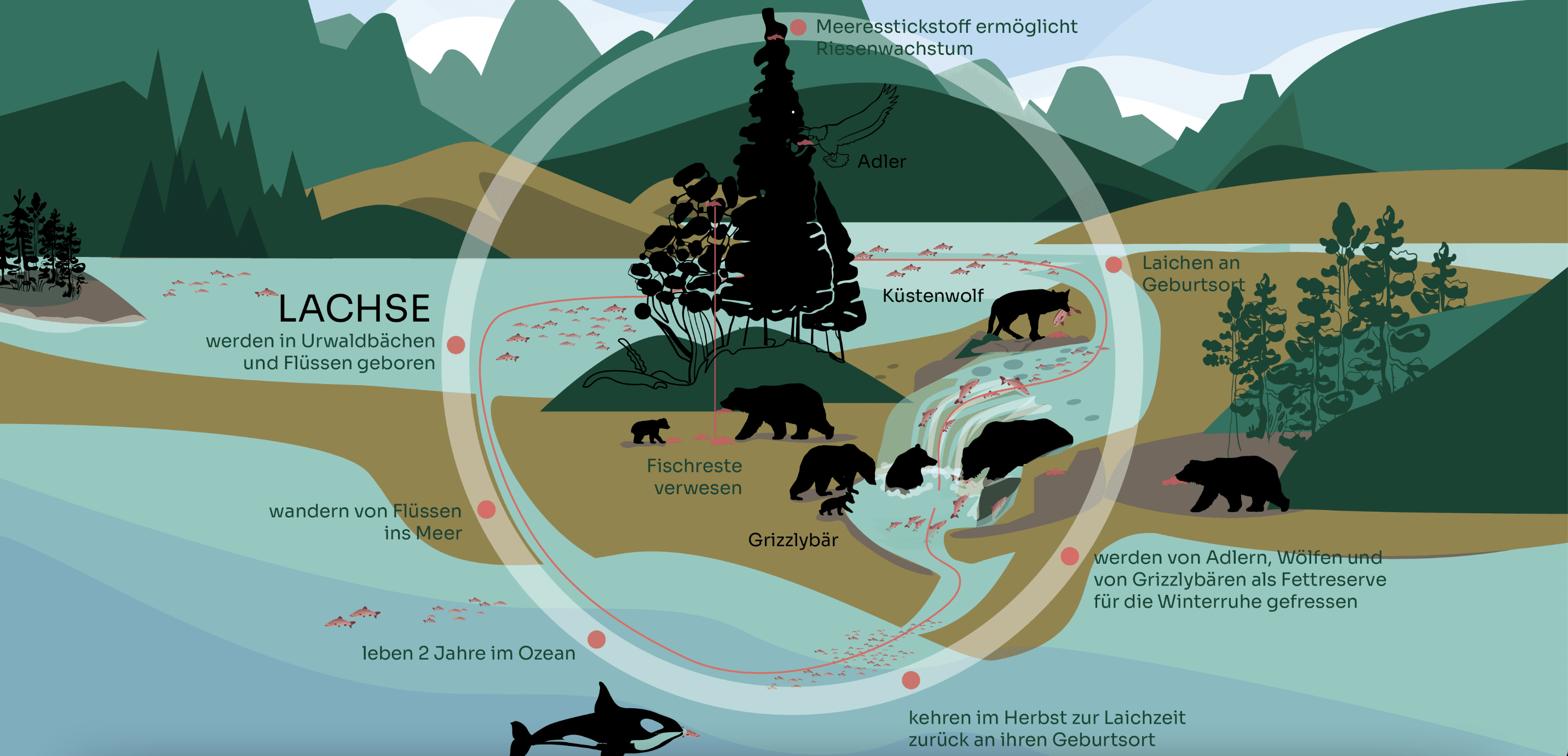
Figure 3 - Salmon cycle
Cycle of salmon and bears/wolves/eagles
Salmon are born in forest streams
One-fifth of the world's salmon originate in the streams and rivers of Western Canada's temperate rainforest region!
This is where one of the most important cycles that keeps the West Coast alive begins and ends. This is where the salmon are born and from here they migrate to the sea.
The rainforest plays an important role in keeping the salmon's birth streams healthy and cool. The roots hold the banks together, the trees shade the water and their wood, leaves and needles provide important nutrients.
The salmon migrate into the sea and are food for orcas
Salmon are an important food source in the sea. Orca whales, for example, depend on salmon as their main food source. Especially the chinook salmon, which are particularly sensitive to changes in the ecosystem in their natal streams.
The salmon migrate back to their natal streams and are food for mammals and birds
After two years in the ocean, millions of salmon make the arduous journey back upstream. This is because they want to spawn in the same place where they were born. Up on the rivers, the grizzly bears are already waiting to catch the fish from the water, as they are dependent on the fat reserves for their hibernation. Coastal wolves, ravens and eagles also love the nutritious salmon. They sometimes carry the fish into the forest to eat them there in peace. And because there is an abundance of food, the bears, wolves and eagles usually only select the finest parts of the fish and leave plenty of leftovers.
Important nutrients for trees
The remaining salmon remains decompose and are broken down into their chemical components. The soil is thus enriched with important nutrients, especially nitrogen, by the animals every year. Scientists have even found evidence of nitrogen compounds of marine origin in the highest treetops.
A sensitive cycle
If even a single salmon run is prevented by deforestation and the resulting siltation and rise in temperature in the rivers, or disrupted by the fishing industry, the natural cycle is severely interrupted. The hunters of salmon, i.e. bears, wolves, eagles and orcas, are directly affected by this. If the salmon are missing, they do not have enough food. And if they no longer drag salmon into the forest, there is a lack of important nutrients for plant growth. However, the forest and its rivers are the habitat for the salmon and their hunters. Clear-cutting therefore disrupts the entire cycle.
Protect a piece of temperate rainforest
2. Biodiversity
Why is there such a great diversity of species?
The exact causes of the extraordinarily high biodiversity in temperate rainforests are still the subject of scientific research.
However, factors such as undisturbed development over millions of years, year-round sunlight, high rainfall, mild climatic conditions and optimal nutrient supply appear to play an important role.
All this led to a complex vegetation structure and a multitude of ecological niches. A wide range of animals specialized in the various layers of the forest, resulting in long food cycles and interactions. Undisturbed by human influence, this has ultimately led to an ever-increasing diversity of species over the course of the earth's history.
Graphic 4 - Wolf's den
Episode 2: Wolves (planned 16.12.)
GRAPHICS/SYMBOLS/Illustrations Highlight most important/exciting species
Inform yourself
Become active
We have to start stopping.
Everyone knows about the value of the Amazon forests and the threat to them. But hardly anyone talks about the forgotten ecosystem of British Columbia, which is home to the last large contiguous area of temperate rainforest in the world. And yet British Columbia, of all places, is one of the last legal areas in the world that continues to allow the large-scale deforestation of 600 to 1,800-year-old primeval forest giants.
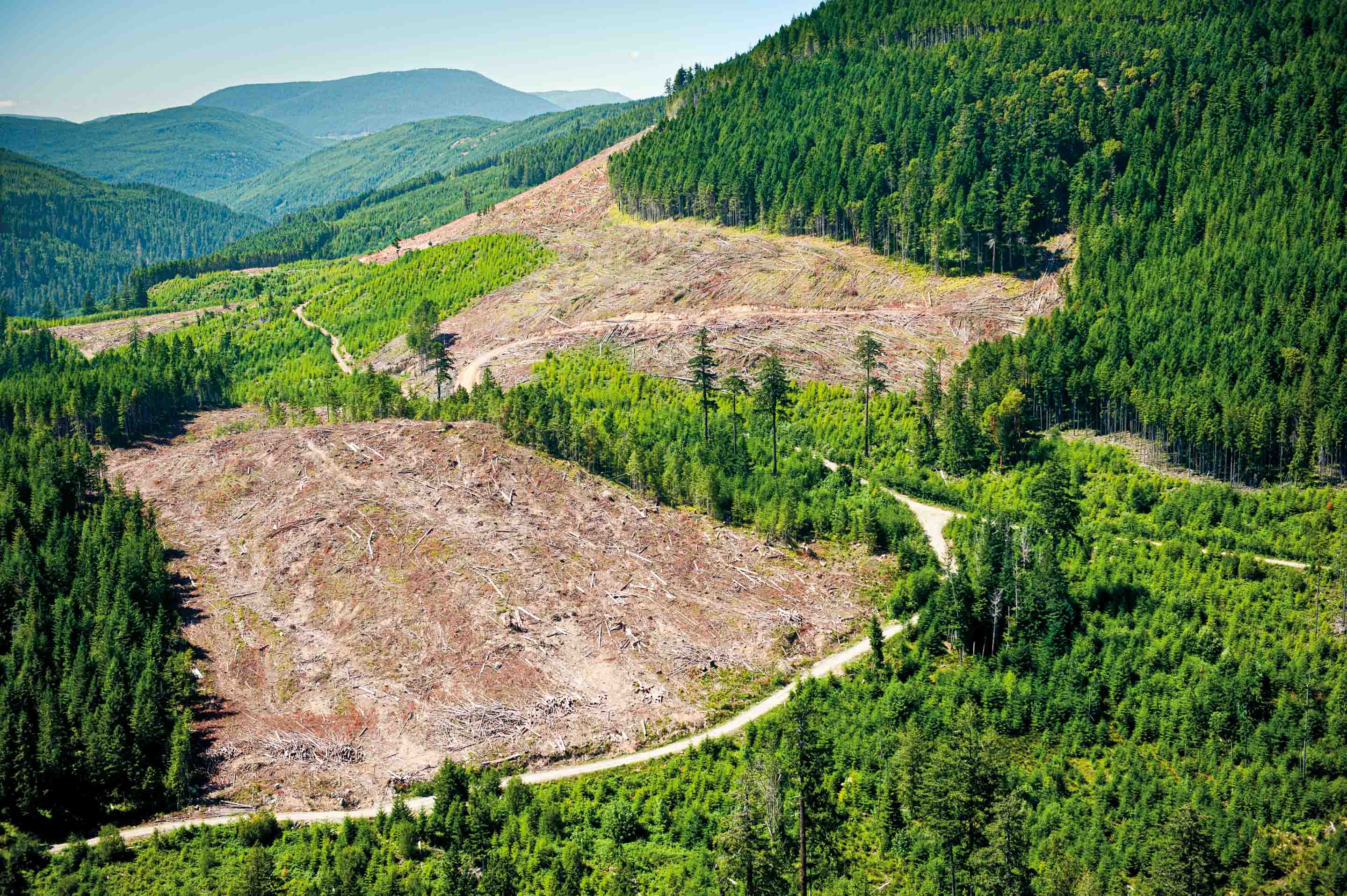

Between 2003 -2010, deforestation in BC was responsible for higher annual CO2 emissions than Finland as a whole. The main causes are the timber industry, agriculture and infrastructure construction.
Why WI protects forests in Canada
Are there any primeval forests left?
70% of Canada is made up of large natural areas. 34% of the country is covered by forest, 53% of which is old-growth forest. In total, Canada is home to 20% of the world's remaining wilderness areas.
Are the existing habitats important for the preservation of biodiversity?
The temperate rainforest is considered the most species-rich ecosystem in the temperate climate zone. Its primeval forests are home to a unique diversity of species and giant trees that are thousands of years old. Rare ghost flowers are at home here, as well as bears, wolves and eagles.
Is the ecosystem relevant for a healthy climate?
The forests in our protected areas are absolute masters of CO2 storage and one of the most important "sinks" in the Earth's carbon cycle. They also make an important contribution to cooling and purifying the air and storing water.
Property rights: Can we buy land with legal certainty and protect it in the long term?
Canada is a constitutional state with strict regulations on property ownership. This makes arbitrary expropriation impossible. Damage entails extensive sanctions. The British Columbia Trespass Act clearly prohibits trespassing on private
land. Violations are prosecuted in court.
Globally, primeval forests are our most important buffer against man-made climate change. Protecting them is a top priority if we want to save the climate.
Kai Andersch
Forest scientist, Chairman of the Board
About WI
We buy wilderness areas and protect them for all future generations - legally secure and with a long-term land register entry.
Donations refinance the purchases and at the same time finance the long-term protection of the areas as well as environmental education projects and research on carbon storage and biodiversity.

As a donor, you will receive a personalized certificate with an aerial photo and the geo-coordinates of your protected forest area - making the impact transparent and traceable.
